Kafka源码-网络层
开篇诗两句:
人生若只如初见,何事秋风悲画扇。
等闲变却故人心,却道故人心易变。 ——纳兰性德《木兰花·拟古决绝词柬友》
SocketServer
1.1 SocketServer启动
SocketServer启动之前主要涉及到3个配置:
listeners:broker配置的所有listener(例如:PLAINTEXT://10.42.80.22:9092)
control.plane.listener.name:控制请求使用的listener
listener.security.protocol.map:各个listener对应的安全协议
SocketServer启动过程,首先创建控制请求对应的Acceptor和Processor,这个创建时根据control.plane.listener.name创建的,如果这个参数没有配置,则不会创建对应的Acceptor和Processors,此时,控制请求会使用数据请求的Acceptor和Processor。
创建控制请求对应的线程模型之后,会创建数据模型的线程模型。数据请求的线程模型的创建也是根据listener创建的,从listeners中排除control.plane.listener.name之后,都是数据请求的listener。
def startup(startProcessingRequests: Boolean = true,
controlPlaneListener: Option[EndPoint] = config.controlPlaneListener,
dataPlaneListeners: Seq[EndPoint] = config.dataPlaneListeners): Unit = {
this.synchronized {
createControlPlaneAcceptorAndProcessor(controlPlaneListener)
createDataPlaneAcceptorsAndProcessors(config.numNetworkThreads, dataPlaneListeners)
if (startProcessingRequests) {
this.startProcessingRequests()
}
}
......
}
1.1.1 控制请求的线程模型和数据请求的线程模型的不同点:
控制请求的线程模型最多只有1个,如果没有配置control.plane.listener.name参数,则不会创建。数据请求的线程模型根据listener配置,可以有多个。
同时,控制请求的线程模型的Acceptor只有1个Processor线程对应,数据请求的线程模型中,Acceptor线程可以对应多个Processor线程,具体数量是通过num.network.threads配置的。
1.1.2 相关参数
控制请求:
// control-plane
private var controlPlaneProcessorOpt : Option[Processor] = None
private[network] var controlPlaneAcceptorOpt : Option[Acceptor] = None
val controlPlaneRequestChannelOpt: Option[RequestChannel] = config.controlPlaneListenerName.map(_ =>
new RequestChannel(20, ControlPlaneMetricPrefix, time, apiVersionManager.newRequestMetrics))
数据请求:
// data-plane
private val dataPlaneProcessors = new ConcurrentHashMap[Int, Processor]()
private[network] val dataPlaneAcceptors = new ConcurrentHashMap[EndPoint, Acceptor]()
val dataPlaneRequestChannel = new RequestChannel(maxQueuedRequests, DataPlaneMetricPrefix, time, apiVersionManager.newRequestMetrics)
1.2 Acceptor线程
创建Acceptor线程需要涉及两个配置参数:socket.send.buffer.bytes和socket.receive.buffer.bytes
Acceptor线程有两个重要的属性,nioSelector和serverChannel,这两个属性需要在初始化时进行创建。serverChannel就是ServerSocketChannel,创建的时候需要指定socket.receive.buffer.bytes
1.2.1 执行逻辑
Acceptor线程主要的工作是将serverChannel接受的连接请求,分发给Processor线程进行处理,具体逻辑如下:
def run(): Unit = {
serverChannel.register(nioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)
startupComplete()
try {
while (isRunning) {
try {
acceptNewConnections()
closeThrottledConnections()
}
catch {
// We catch all the throwables to prevent the acceptor thread from exiting on exceptions due
// to a select operation on a specific channel or a bad request. We don't want
// the broker to stop responding to requests from other clients in these scenarios.
case e: ControlThrowable => throw e
case e: Throwable => error("Error occurred", e)
}
}
} finally {
debug("Closing server socket, selector, and any throttled sockets.")
CoreUtils.swallow(serverChannel.close(), this, Level.ERROR)
CoreUtils.swallow(nioSelector.close(), this, Level.ERROR)
throttledSockets.foreach(throttledSocket => closeSocket(throttledSocket.socket))
throttledSockets.clear()
shutdownComplete()
}
}
private def acceptNewConnections(): Unit = {
val ready = nioSelector.select(500)
if (ready > 0) {
val keys = nioSelector.selectedKeys()
val iter = keys.iterator()
while (iter.hasNext && isRunning) {
try {
val key = iter.next
iter.remove()
if (key.isAcceptable) {
accept(key).foreach { socketChannel =>
// Assign the channel to the next processor (using round-robin) to which the
// channel can be added without blocking. If newConnections queue is full on
// all processors, block until the last one is able to accept a connection.
var retriesLeft = synchronized(processors.length)
var processor: Processor = null
do {
retriesLeft -= 1
processor = synchronized {
// adjust the index (if necessary) and retrieve the processor atomically for
// correct behaviour in case the number of processors is reduced dynamically
currentProcessorIndex = currentProcessorIndex % processors.length
processors(currentProcessorIndex)
}
currentProcessorIndex += 1
} while (!assignNewConnection(socketChannel, processor, retriesLeft == 0))
}
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized key state for acceptor thread.")
} catch {
case e: Throwable => error("Error while accepting connection", e)
}
}
}
}
(1)首先在nioSelector上注册OP_ACCEPT事件
(2)循环执行,nioSelector选择准备好的key(这里只注册了一个),如果时请求连接事件,serverChannel接受请求,并将socketChannel提交给Processor线程处理
因为一个Acceptor线程是可能对应多个Processor线程的,分配的时候采用的是round-robin的方式,如果当前选择的Processor不能处理这个请求,便会重试,重试次数为Processor线程的数量。(如果所有的Processor线程都无法处理这个socketChannel,就会阻塞,直到最后一个Processer能够处理这个请求)
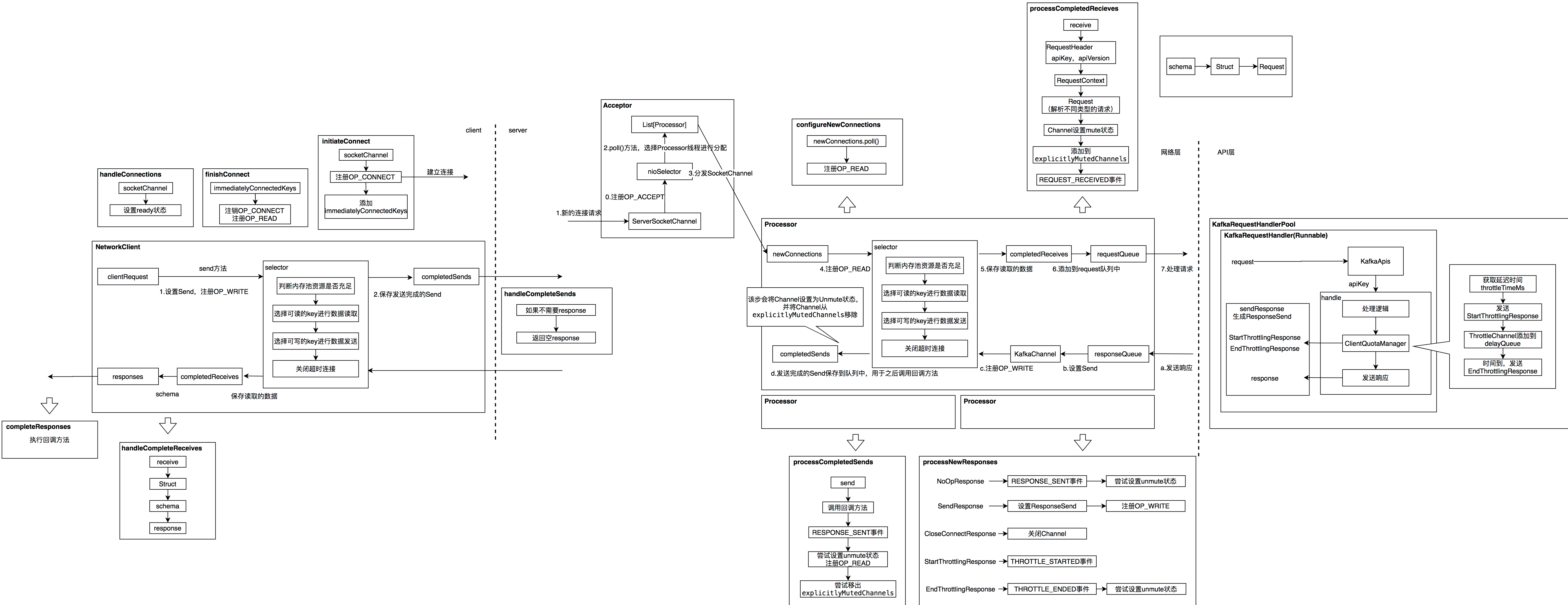
1.3 Processor线程
Processor线程有如下几个重要属性:
private val newConnections = new ArrayBlockingQueue[SocketChannel](connectionQueueSize)
private val inflightResponses = mutable.Map[String, RequestChannel.Response]()
private val responseQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque[RequestChannel.Response]()
newConnections是一个阻塞队列,主要的作用的Acceptor线程为Processor线程分配链接时,会将SocketChannel放到对应的Processor的这个队列中。
inflightResponses:记录各个connect正在发送的response。
responseQueue也是一个阻塞队列,主要的作用是请求处理完成之后,会将response放到这个队列中,Processor线程会从这个队列中获取response,并注册Selector状态,将response发送出去。
每个Processor线程都有独立的selector来处理READ事件和WRITE事件:
private val selector = createSelector(
ChannelBuilders.serverChannelBuilder(
listenerName,
listenerName == config.interBrokerListenerName,
securityProtocol,
config,
credentialProvider.credentialCache,
credentialProvider.tokenCache,
time,
logContext,
() => apiVersionManager.apiVersionResponse(throttleTimeMs = 0)
)
)
1.3.1 执行逻辑
Processor线程的主要执行逻辑如下:
(1)configureNewConnections()方法:主要的工作是从newConnections中获取Acceptor线程分配的SocketChannel,在selector上注册监听OP_READ事件。(这个方法很简单不详细描述)
(2)processNewResponses()方法:主要的工作是从responseQueue中获取response,将response设置为SocketChannel的Send,并设置OP_WRITE事件,后面会详细描述。
(3)poll()方法:执行selector.poll方法,监听各个channel的状态来执行对应的读写事件
(4)processCompletedReceives()方法:将接收到的request添加到requestQueue中,共RequestHandler线程获取,并将channel设置成Mute状态,保证每个channel相同时间只有一个请求在处理
(5)processCompletedSends()方法:Send对象成功发送之后的处理逻辑,调用回调方法,解除Channel的Mute状态
(6)processDisconnected()方法:连接断开的处理逻辑,不详细描述
(7)closeExcessConnections()方法:关闭连接的处理逻辑,不详细描述
override def run(): Unit = {
startupComplete()
try {
while (isRunning) {
try {
// setup any new connections that have been queued up
configureNewConnections()
// register any new responses for writing
processNewResponses()
poll()
processCompletedReceives()
processCompletedSends()
processDisconnected()
closeExcessConnections()
} catch {
// We catch all the throwables here to prevent the processor thread from exiting. We do this because
// letting a processor exit might cause a bigger impact on the broker. This behavior might need to be
// reviewed if we see an exception that needs the entire broker to stop. Usually the exceptions thrown would
// be either associated with a specific socket channel or a bad request. These exceptions are caught and
// processed by the individual methods above which close the failing channel and continue processing other
// channels. So this catch block should only ever see ControlThrowables.
case e: Throwable => processException("Processor got uncaught exception.", e)
}
}
} finally {
debug(s"Closing selector - processor $id")
CoreUtils.swallow(closeAll(), this, Level.ERROR)
shutdownComplete()
}
}
1.3.2 processNewResponses()方法
private def processNewResponses(): Unit = {
var currentResponse: RequestChannel.Response = null
while ({currentResponse = dequeueResponse(); currentResponse != null}) {
val channelId = currentResponse.request.context.connectionId
try {
currentResponse match {
case response: NoOpResponse =>
// There is no response to send to the client, we need to read more pipelined requests
// that are sitting in the server's socket buffer
updateRequestMetrics(response)
trace(s"Socket server received empty response to send, registering for read: $response")
// Try unmuting the channel. If there was no quota violation and the channel has not been throttled,
// it will be unmuted immediately. If the channel has been throttled, it will be unmuted only if the
// throttling delay has already passed by now.
handleChannelMuteEvent(channelId, ChannelMuteEvent.RESPONSE_SENT)
tryUnmuteChannel(channelId)
case response: SendResponse =>
sendResponse(response, response.responseSend)
case response: CloseConnectionResponse =>
updateRequestMetrics(response)
trace("Closing socket connection actively according to the response code.")
close(channelId)
case _: StartThrottlingResponse =>
handleChannelMuteEvent(channelId, ChannelMuteEvent.THROTTLE_STARTED)
case _: EndThrottlingResponse =>
// Try unmuting the channel. The channel will be unmuted only if the response has already been sent out to
// the client.
handleChannelMuteEvent(channelId, ChannelMuteEvent.THROTTLE_ENDED)
tryUnmuteChannel(channelId)
case _ =>
throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"Unknown response type: ${currentResponse.getClass}")
}
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
processChannelException(channelId, s"Exception while processing response for $channelId", e)
}
}
}
processNewResponses()方法主要的工作是从responseQueue中获取response,并根据具体的类型进行不同的处理:
(1)NoOpResponse:表示没有response发送到client,需要触发ChannelMuteEvent.RESPONSE_SENT事件来修改KafkaChannel的状态(KafkaChannel是SocketChannel的封装),之后尝试解除当前Channel的Mute状态,该操作只会在当前状态为ChannelMuteState.MUTED执行,并注册OP_READ事件。(状态转换后面介绍)
(2)SendResponse:表示需要发送response给client,调用sendResponse方法,该方法并不是真的将消息进行发送,而是在Selector上注册OP_WRITE事件。
protected[network] def sendResponse(response: RequestChannel.Response, responseSend: Send): Unit = {
val connectionId = response.request.context.connectionId
trace(s"Socket server received response to send to $connectionId, registering for write and sending data: $response")
// `channel` can be None if the connection was closed remotely or if selector closed it for being idle for too long
if (channel(connectionId).isEmpty) {
warn(s"Attempting to send response via channel for which there is no open connection, connection id $connectionId")
response.request.updateRequestMetrics(0L, response)
}
// Invoke send for closingChannel as well so that the send is failed and the channel closed properly and
// removed from the Selector after discarding any pending staged receives.
// `openOrClosingChannel` can be None if the selector closed the connection because it was idle for too long
if (openOrClosingChannel(connectionId).isDefined) {
selector.send(new NetworkSend(connectionId, responseSend))
inflightResponses += (connectionId -> response)
}
}
(3)CloseConnectionResponse:关闭链接。
(4)StartThrottlingResponse:设置限流状态。
(5)EndThrottlingResponse:结束限流状态,并且尝试解除Channel的静音状态。
1.3.3 poll()方法
private def poll(): Unit = {
val pollTimeout = if (newConnections.isEmpty) 300 else 0
try selector.poll(pollTimeout)
catch {
case e @ (_: IllegalStateException | _: IOException) =>
// The exception is not re-thrown and any completed sends/receives/connections/disconnections
// from this poll will be processed.
error(s"Processor $id poll failed", e)
}
}
该方法主要是调用selector.poll()方法来处理所有准备完成的Channel事件。
selector.poll()方法代卖比较长,这里没有贴出,该方法主要的工作总结如下:
(1)判断当前缓存池资源是否充足,如果足够,就尝试解除Channel的状态,(要求不能在explicitlyMutedChannels中)
(2)首先判断当前状态需不需要处理数据,判断条件有三个:
a)准备好的SelectionKey的数量大于0
b)需要立即处理的链接列表不为空
c)缓存中存在数据需要读(PLAINTAXT没有缓存数据,加密传输方式会有缓存)
(3)如果满足(1)中的条件,或获取所有需要处理的SelectionKey,然后调用pollSelectionKeys()方法进行数据读取或者数据发送。
对于需要从缓存中读取数据的key,不是通过Selector的selectedKeys方法获取的,而是在上一次的poll操作中,将缓存中存在数据的key保存在了keysWithBufferedRead列表中。
pollSelectionKeys()方法的主要处理逻辑是:
a)首先判断channel的数据是否准备好,(这里的判断是针对加密传入的判断,明文传输方式直接就是准备完成的状态),如果没有准备完成,会执行channel.prepare()。
b)尝试读取数据,读取数据时所使用的缓存是从创建Processor线程时传入缓存池中获取的,如果缓存池资源不足,会Mute当前Channel来缓解内存压力。读取的请求数据会保存到stagedReceives
c)判断当前channel如果存在缓存数据需要读取,添加到keysWithBufferedRead,方便下次poll操作时获取。
d)尝试写消息,将上一步processNewResponses()方法设置的Send对象发送出去,并将发送完成的Send对象保存到completedSends。
(4)关闭超时的连接
(5)从stagedReceives中获取请求的数据,放到completedReceives中,每个Channel每次只能处理一个请求,如果Channel是Mute状态,则跳过操作。
1.3.4 processCompletedReceives()方法
private def processCompletedReceives(): Unit = {
selector.completedReceives.forEach { receive =>
try {
openOrClosingChannel(receive.source) match {
case Some(channel) =>
val header = parseRequestHeader(receive.payload)
if (header.apiKey == ApiKeys.SASL_HANDSHAKE && channel.maybeBeginServerReauthentication(receive,
() => time.nanoseconds()))
trace(s"Begin re-authentication: $channel")
else {
val nowNanos = time.nanoseconds()
if (channel.serverAuthenticationSessionExpired(nowNanos)) {
// be sure to decrease connection count and drop any in-flight responses
debug(s"Disconnecting expired channel: $channel : $header")
close(channel.id)
expiredConnectionsKilledCount.record(null, 1, 0)
} else {
val connectionId = receive.source
val context = new RequestContext(header, connectionId, channel.socketAddress,
channel.principal, listenerName, securityProtocol,
channel.channelMetadataRegistry.clientInformation, isPrivilegedListener, channel.principalSerde)
val req = new RequestChannel.Request(processor = id, context = context,
startTimeNanos = nowNanos, memoryPool, receive.payload, requestChannel.metrics, None)
// KIP-511: ApiVersionsRequest is intercepted here to catch the client software name
// and version. It is done here to avoid wiring things up to the api layer.
if (header.apiKey == ApiKeys.API_VERSIONS) {
val apiVersionsRequest = req.body[ApiVersionsRequest]
if (apiVersionsRequest.isValid) {
channel.channelMetadataRegistry.registerClientInformation(new ClientInformation(
apiVersionsRequest.data.clientSoftwareName,
apiVersionsRequest.data.clientSoftwareVersion))
}
}
requestChannel.sendRequest(req)
selector.mute(connectionId)
handleChannelMuteEvent(connectionId, ChannelMuteEvent.REQUEST_RECEIVED)
}
}
case None =>
// This should never happen since completed receives are processed immediately after `poll()`
throw new IllegalStateException(s"Channel ${receive.source} removed from selector before processing completed receive")
}
} catch {
// note that even though we got an exception, we can assume that receive.source is valid.
// Issues with constructing a valid receive object were handled earlier
case e: Throwable =>
processChannelException(receive.source, s"Exception while processing request from ${receive.source}", e)
}
}
selector.clearCompletedReceives()
}
processCompletedReceives()方法主要的工作是从上一步中的completedReceives中获取请求数据,并发送到RequestChannel中
之后将Channel设置成Mute状态,并且添加到explicitlyMutedChannels,并且对当前的Channel设置ChannelMuteEvent.REQUEST_RECEIVED事件。
1.3.5 processCompletedSends()方法
private def processCompletedReceives(): Unit = {
selector.completedReceives.forEach { receive =>
try {
openOrClosingChannel(receive.source) match {
case Some(channel) =>
val header = parseRequestHeader(receive.payload)
if (header.apiKey == ApiKeys.SASL_HANDSHAKE && channel.maybeBeginServerReauthentication(receive,
() => time.nanoseconds()))
trace(s"Begin re-authentication: $channel")
else {
val nowNanos = time.nanoseconds()
if (channel.serverAuthenticationSessionExpired(nowNanos)) {
// be sure to decrease connection count and drop any in-flight responses
debug(s"Disconnecting expired channel: $channel : $header")
close(channel.id)
expiredConnectionsKilledCount.record(null, 1, 0)
} else {
val connectionId = receive.source
val context = new RequestContext(header, connectionId, channel.socketAddress,
channel.principal, listenerName, securityProtocol,
channel.channelMetadataRegistry.clientInformation, isPrivilegedListener, channel.principalSerde)
val req = new RequestChannel.Request(processor = id, context = context,
startTimeNanos = nowNanos, memoryPool, receive.payload, requestChannel.metrics, None)
// KIP-511: ApiVersionsRequest is intercepted here to catch the client software name
// and version. It is done here to avoid wiring things up to the api layer.
if (header.apiKey == ApiKeys.API_VERSIONS) {
val apiVersionsRequest = req.body[ApiVersionsRequest]
if (apiVersionsRequest.isValid) {
channel.channelMetadataRegistry.registerClientInformation(new ClientInformation(
apiVersionsRequest.data.clientSoftwareName,
apiVersionsRequest.data.clientSoftwareVersion))
}
}
requestChannel.sendRequest(req)
selector.mute(connectionId)
handleChannelMuteEvent(connectionId, ChannelMuteEvent.REQUEST_RECEIVED)
}
}
case None =>
// This should never happen since completed receives are processed immediately after `poll()`
throw new IllegalStateException(s"Channel ${receive.source} removed from selector before processing completed receive")
}
} catch {
// note that even though we got an exception, we can assume that receive.source is valid.
// Issues with constructing a valid receive object were handled earlier
case e: Throwable =>
processChannelException(receive.source, s"Exception while processing request from ${receive.source}", e)
}
}
selector.clearCompletedReceives()
}
首先从inflightResponses中移除当前已经成功发送的请求,然后调用回调方法。
对当前的Channel处理ChannelMuteEvent.RESPONSE_SENT事件,并且尝试解除Channel的Mute状态,并且从explicitlyMutedChannels中移除。
线程模型